Structure Gallery
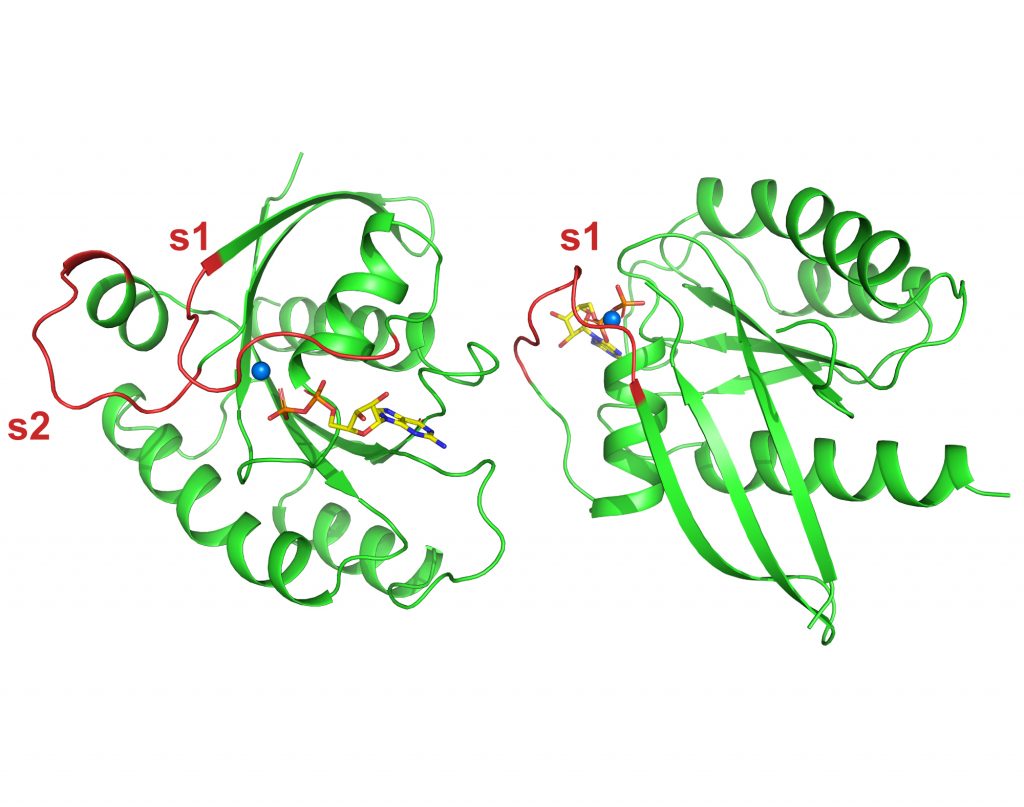
KRAS4B WT GDP
To be published
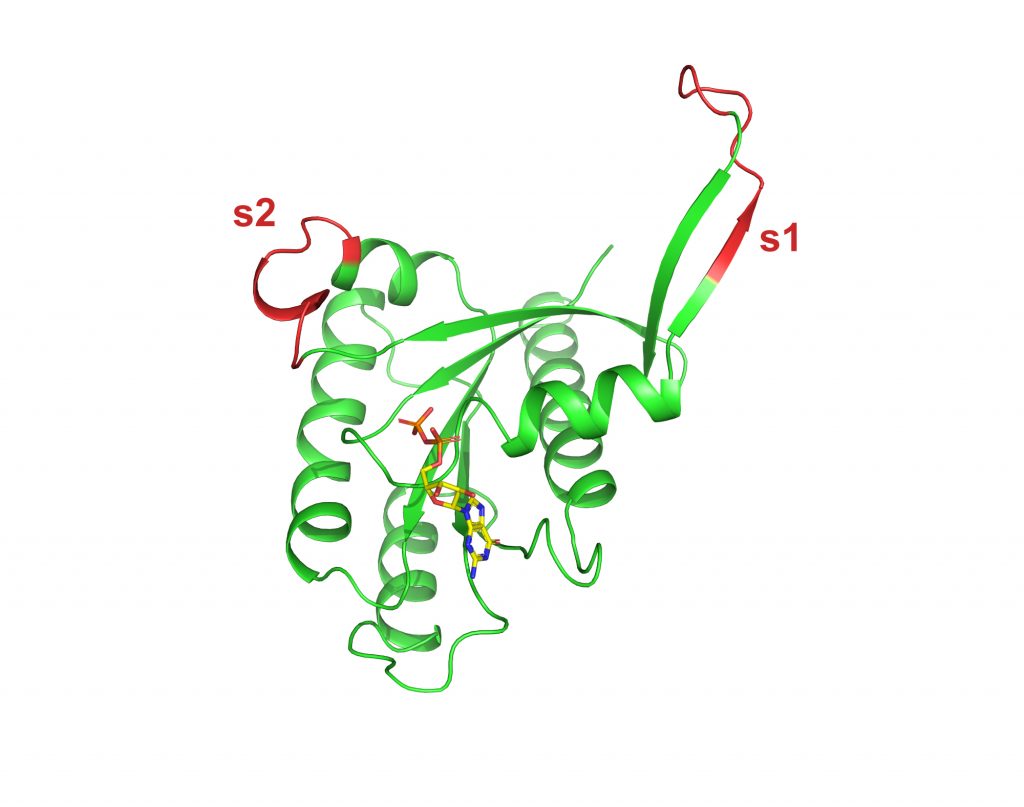
KRAS4B A146T GDP
To be published
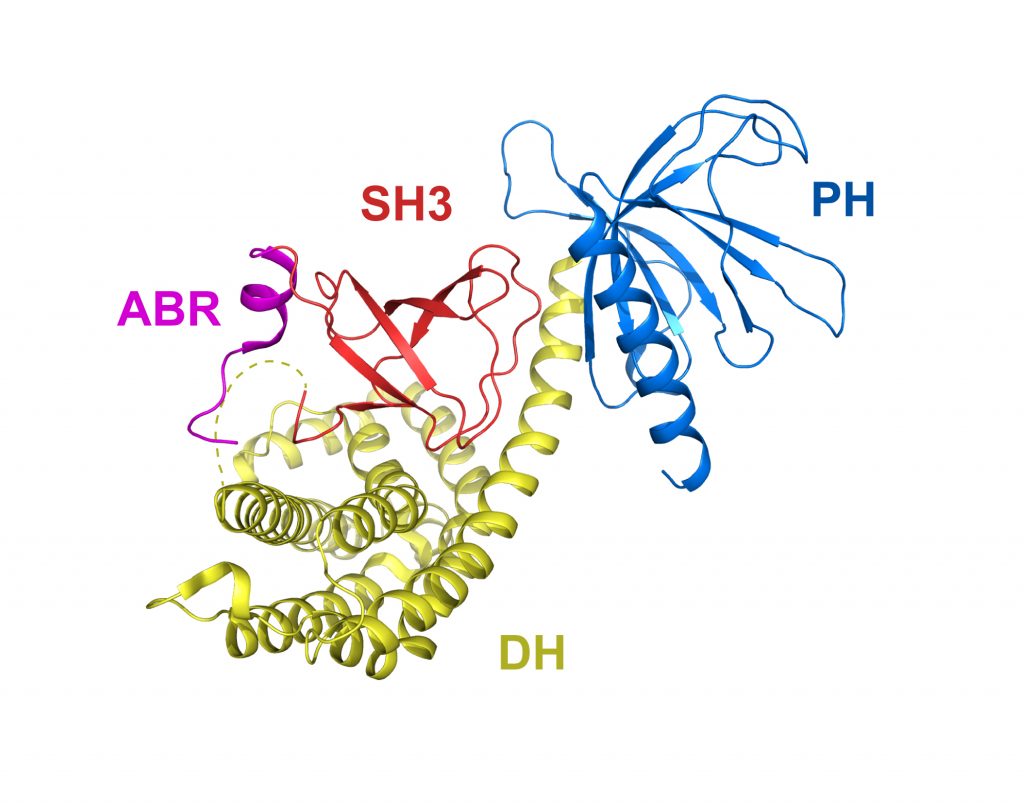
Auto-inhibited Asef
PDB: 2PZ1
Mitin et al. (2007). Release of auto-inhibition of Asef by APC leads to Cdc42 activation and tumor suppression. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 9, 814-823. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb1290
Structural determination of autoinhibited ASEF reveals that the SH3 domain forms an extensive interface with the catalytic DH and PH domains to obstruct binding and activation of CDC42, and the CAB motif is positioned adjacent to the SH3 domain to facilitate activation by APC. In colorectal cancer cell lines, APC activates CDC42 in an ASEF-dependent manner to suppress anchorageindependent growth.
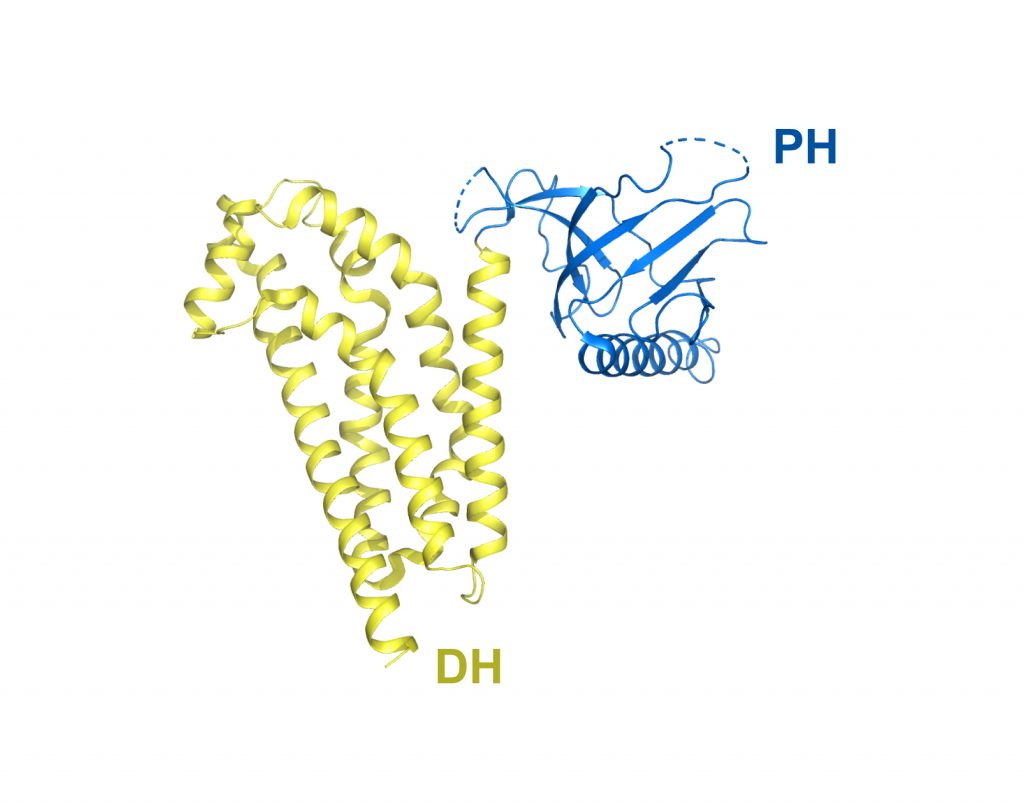
DH/PH fragment of Dbs without bound GTPase
PDB: 1RJ2
Worthylake et al. (2004). Crystal structure of the DH/PH fragment of Dbs without bound GTPase. Structure 12, 1078-85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2004.03.021
The structure of the unbound form of the DH/PH of Dbs is similar to the structures of Dbs bound to GTPases albeit with greater apparent mobility between the DH and PH domains. These comparisons suggest that the DH and PH domains of Dbs are spatially primed for binding GTPases and small alterations in intradomain conformations that may be elicited by subtle biological responses, such as altered phosphoinositide levels, are sufficient to enhance exchange by facilitating interactions between the PH domain and GTPases.
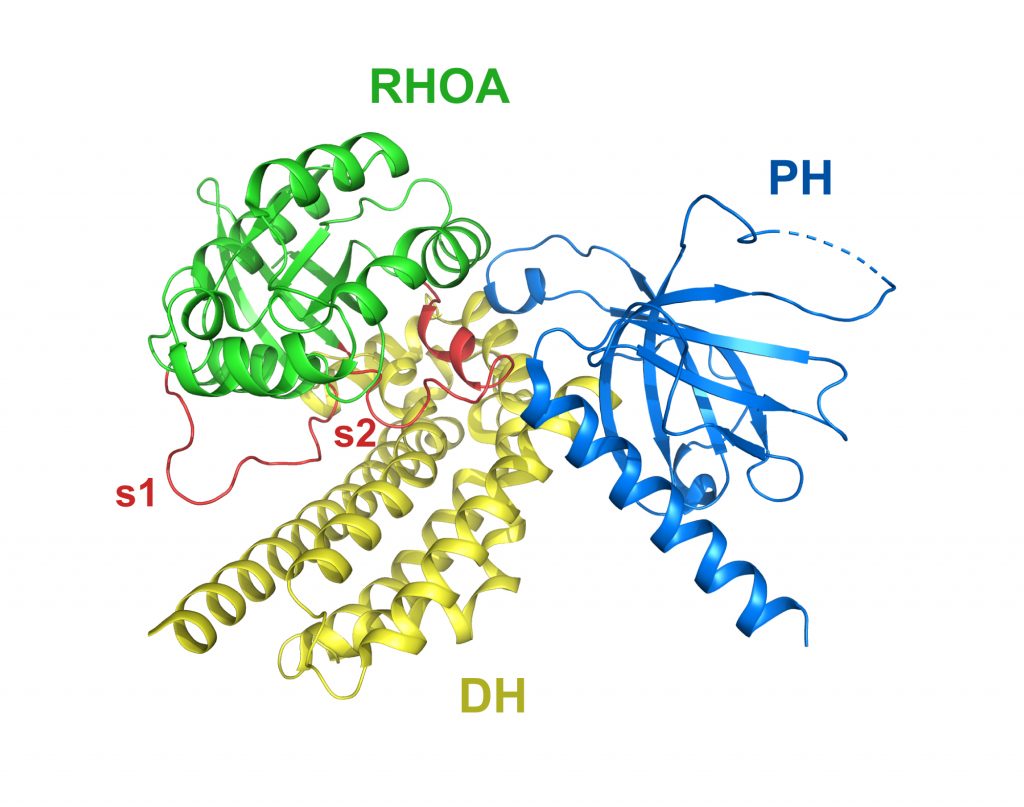
Dbl and Pleckstrin homology domains of Dbs in complex with RHOA
PDB: 1LB1
Snyder et al. (2002). Structural basis for the selective activation of Rho GTPases by Dbl exchange factors. Nat. Struct. Biol. 9, 468-475. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb796
The crystal structures of the conserved, catalytic DH/PH fragments of the exchange factors Dbs, ITSN and Tiam1 with their cognate GTPases, CDC42, RHOA and RAC1 reveal the key determinants responsible for promoting GTPase-selective exchange activity among Dbl family RHOGEFs.
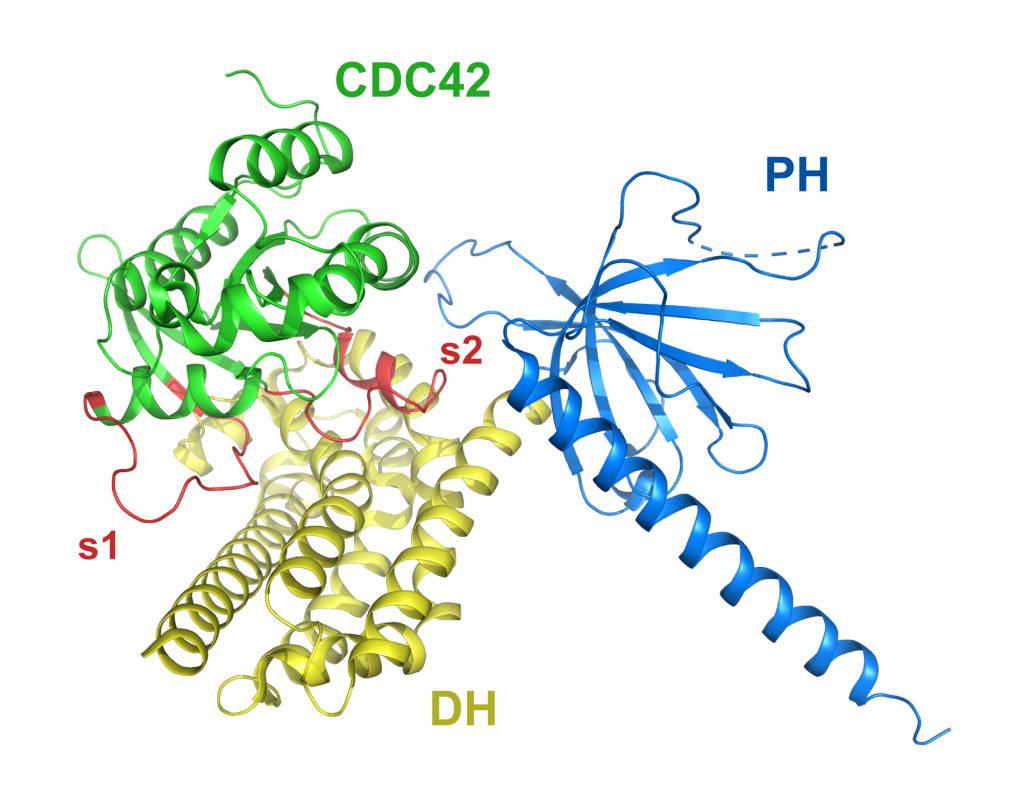
Dbs DH/PH(Y889F) bound to nucleotide-free CDC42
PDB: 1KZG
Rossman et al. (2002). A crystallographic view of interactions between Dbs and Cdc42: PH domain-assisted guanine nucleotide exchange. EMBO J. 21, 1315-26. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/21.6.1315
The crystal structure of the DH/PH fragment from Dbs in complex with CDC42 features the PH domain in a unique conformation that allows direct interaction with CDC42 required for efficient exchange activity. Y889F in the PH domain removes a key hydrogen bound between the PH domain and CDC42 necessary for full exchange activity, with essentially no structural impact on the complex.
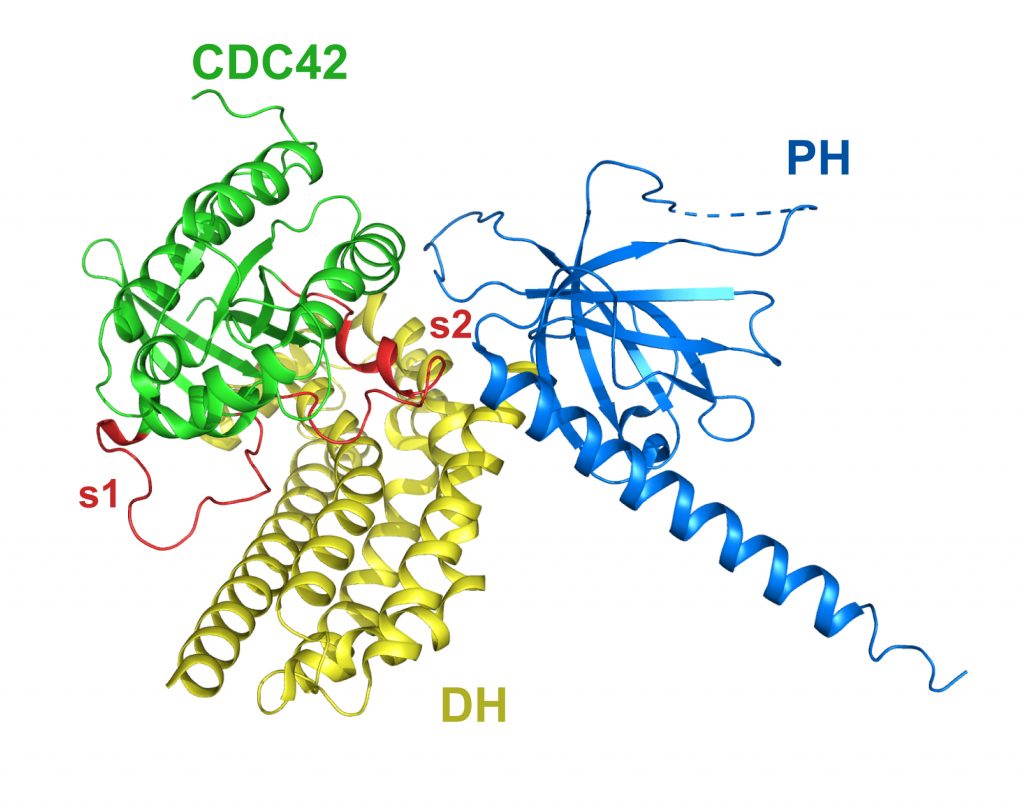
DH/PH fragment of murine Dbs in complex with the placental isoform of human CDC42
PDB: 1KZ7
Rossman et al. (2002). A crystallographic view of interactions between Dbs and CDC42: PH domain-assisted guanine nucleotide exchange. EMBO J. 21, 1315-26. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/21.6.1315
Biochemical data indicate that for some Dbl‐family proteins, PH domains may cooperate with their associated DH domains in promoting guanine nucleotide exchange of Rho GTPases. The crystal structure of the DH/PH fragment from Dbs in complex with CDC42 features the PH domain in a unique conformation that allows direct interaction with CDC42 required for efficient exchange activity.
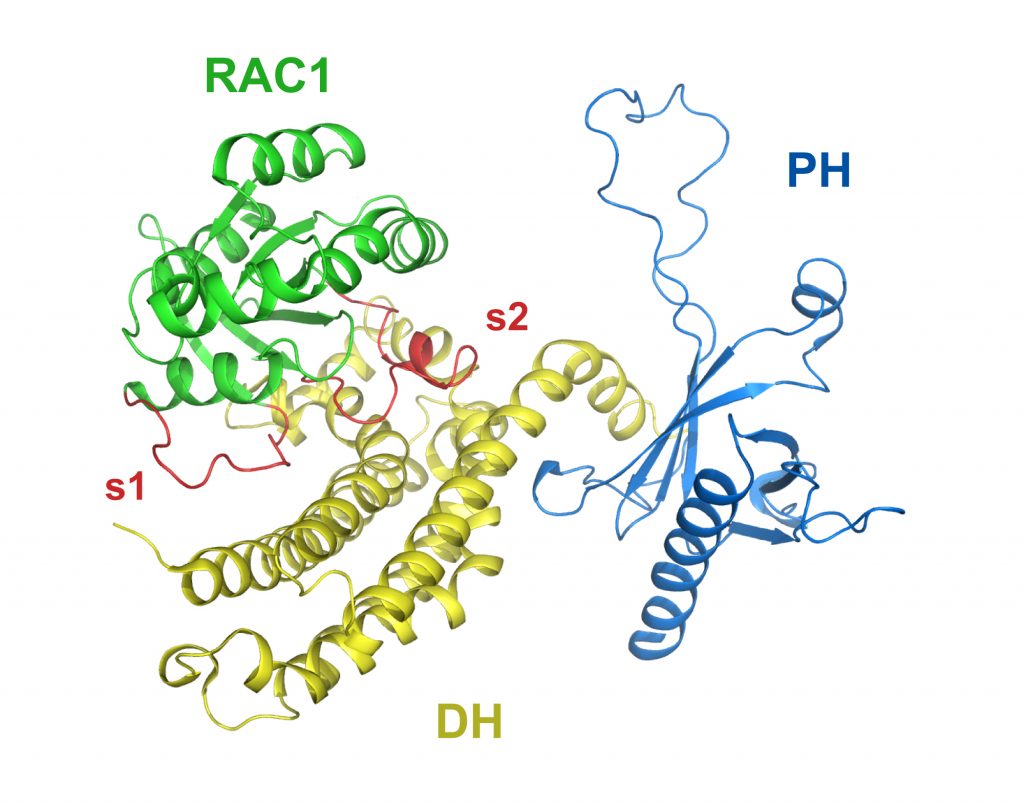
RAC1 in complex with the guanine nucleotide exchange region of Tiam1
PDB: 1FOE
Worthylake et al. (2000). Crystal structure of RAC1 in complex with the guanine nucleotide exchange region of Tiam1. Nature 408, 682-8. https://doi.org/10.1038/35047014
The first structural characterization of a Dbl family RHOGEF bound to a RHO GTPase. The crystal structure of the DH and PH domains of the T-lymphoma invasion and metastasis factor 1 (Tiam1) protein in complex with its cognate RHO family GTPase, RAC1, highlights the interactions and mechanism necessary for Dbl-catalyzed nucleotide exchange of RHO GTPases.

